Delving into the intricate tapestry of artistic vision, one inevitably stumbles upon the enigmatic existence of Ayn Rand. An illustrious luminary, whose brilliance still reverberates through the annals of time, Rand remains an unmistakable symbol of audacity and unbridled imagination. Within her fervent embrace of the written word, a symphony of thoughts and emotions unfolds, captivating readers with its sheer power and defiance of societal norms.
With a passionate fervor that knows no bounds, Rand fearlessly pursued her penmanship, weaving together tales of tenacious protagonists whose struggles mirror the very essence of our human condition. Each stroke of her literary brush unleashes a tempestuous storm of ideas, challenging the status quo and intertwining philosophy with art to form a breathtaking tapestry of intellectual liberation.
Like the brushstrokes of a master painter, Rand's words paint vivid pictures, engulfing the reader in a world teeming with idiosyncratic complexities and moral dilemmas. Her incisive prose pulls at the heartstrings of readers, unveiling the depths of human existence through the protagonists' relentless pursuit of individuality and unwavering commitment to personal freedom.
Within the very fiber of her creations lies a reverence for the human spirit, an indomitable force that surges forth, unyielding to the pressures of conformity. Rand's oeuvre resonates as a poignant reminder of the transformative power of the individual, an echo that reverberates through the corridors of time, challenging readers to reflect upon their own beliefs and question the limitations imposed upon their dreams.
Ayn Rand: A Visionary Author and Philosopher

Unlocking the depths of human thought and exploring the complexities of existence, Ayn Rand emerges as a profound visionary whose literary works and philosophical ideas captivate readers and scholars alike. This section delves into the remarkable qualities that defined Ayn Rand as a multifaceted talent and explores the enduring impact of her ideas.
1. Insightful Literary Prodigy: Ayn Rand's literary prowess lies in her ability to weave intricate narratives that delve into the human psyche and challenge conventional norms. Her books transcend mere storytelling and offer a window into the depths of the human condition, provoking contemplation and introspection in her readers.
2. A Radical Ideologue: Ayn Rand's philosophical theories, prominently showcased in her magnum opus "Atlas Shrugged" and "The Fountainhead," present a radically individualistic ideology advocating for rational self-interest and laissez-faire capitalism. Her ideas continue to stir debates and inspire individuals to question the nature of societal structures.
3. Architect of Objectivism: Ayn Rand's philosophy of Objectivism, encompassing the ethical principles of reason, individualism, and rational self-interest, serves as the foundation for her literary works and philosophical treatises. This section sheds light on the core tenets of Objectivism and their impact on the wider intellectual discourse.
4. Championing Individualism: A central theme in Ayn Rand's writings is the celebration of individualism and the rejection of collectivism. This segment discusses how Rand's bold exploration of the rights and potential of the individual challenges traditional societal constructs and inspires personal empowerment.
5. An Influential Cultural Icon: Ayn Rand's ideas have permeated popular culture and influenced various fields, including economics, politics, and art. This part highlights the lasting influence of Rand's philosophy on contemporary thinkers, artists, and intellectuals, underscoring her enduring legacy.
6. Continued Relevance: Despite the passage of time, Ayn Rand's ideas continue to resonate with a diverse range of individuals seeking intellectual enlightenment and creative inspiration. This section explores the ongoing relevance and applicability of Rand's philosophies in a rapidly evolving world.
7. Ayn Rand's Intellectual Legacy: Beyond her literary and philosophical achievements, this segment explores Ayn Rand's enduring impact as an influential thinker whose intellectual legacy stretches far beyond the realm of literature, shaping the intellectual discourse for generations to come.
Exploring Ayn Rand's Early Life and Influences
Delving into the formative years and influential factors that shaped Ayn Rand's intellectual journey unveils a captivating narrative of her early life. This section takes a closer look at the experiences, environments, and individuals who played a significant role in molding the brilliant mind behind some of the most groundbreaking philosophical works of the 20th century.
- Educational Background: At the core of Ayn Rand's intellectual development lies her educational journey. Growing up in St. Petersburg, Russia, she embraced the pursuit of knowledge at an early age. Immerse yourself in the educational institutions she attended and explore how they instilled a thirst for learning that would propel her future endeavors.
- Influential Figures: No individual exists in isolation, and Ayn Rand's life was no exception. Discover the key figures who left an indelible mark on her worldview and intellectual development. From her family members to esteemed mentors, each person served as a catalyst for her burgeoning ideas.
- Philosophical and Literary Influences: Ayn Rand's ideological framework was not forged in a vacuum. Uncover the philosophical and literary works that influenced her early ideas. From the writings of Nietzsche and Aristotle to the novels of Victor Hugo and Fyodor Dostoevsky, trace the threads that wove together to form the unique tapestry of her philosophy.
- Moving to America: A pivotal moment in Ayn Rand's life occurred when she immigrated to the United States in 1926. Explore the reasons behind her decision to leave her homeland and the impact that America had on shaping her perspectives. Delve into the opportunities and challenges she faced as she embraced her new life in a foreign land.
- Personal Experiences: Beyond the realm of intellectual influences, Ayn Rand's personal experiences, both positive and negative, played a crucial role in shaping her worldview. Examine the defining moments in her life, such as the Russian Revolution and her encounters with individualism and collectivism, to gain deeper insights into the foundations of her philosophy.
By delving into Ayn Rand's early life and influences, a rich tapestry of experiences, education, and people emerges, offering valuable insights into the intellectual force behind her revolutionary ideas. Understanding the journey that led Ayn Rand to become a towering figure in the world of philosophy provides a greater appreciation for the genesis of her unbounded creativity.
The Controversial Concepts of Objectivism
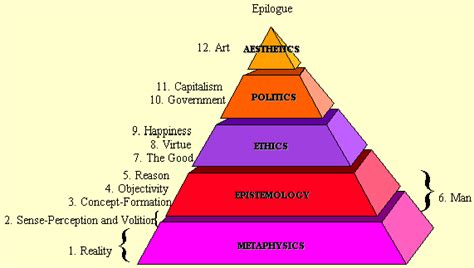
In this section, we delve into the provocative ideas that form the foundation of Objectivism, a philosophical school of thought developed by a renowned and influential thinker. Objectivism challenges conventional wisdom and offers a unique perspective on various aspects of life and society.
One of the central tenets of Objectivism is the notion of rational self-interest, asserting that individuals should prioritize their own well-being and pursue their own happiness above all else. This concept challenges traditional notions of altruism and advocates for a rational approach to personal fulfillment.
Another controversial idea within Objectivism is the concept of laissez-faire capitalism. Objectivists argue for minimal government intervention in the economy, advocating for a free-market system where individuals are free to pursue their economic goals without excessive regulations. This belief often sparks debate and criticism from those who argue for a more interventionist approach to economic affairs.
Objectivism also promotes the importance of reason and individualism. It emphasizes the power of human reason as the ultimate tool for understanding the world and making decisions. Individualism, in this context, emphasizes the sovereignty of the individual and rejects collectivist ideologies that prioritize the needs and rights of the group over those of the individual.
Furthermore, Objectivism challenges conventional moral frameworks, proposing a rational egoism as the basis for ethical decision-making. It posits that individuals should act in their own self-interest, guided by reason, and reject the notion of sacrificing oneself for the sake of others or societal expectations.
These controversial concepts of Objectivism have sparked both admiration and critique. While some view them as a refreshing alternative to conventional wisdom, others perceive them as overly individualistic and dismissive of societal well-being. The ongoing debates surrounding Objectivism highlight the enduring relevance and impact of Ayn Rand's ideas.
The Impact of Ayn Rand's Fiction on Literature and Society
Exploring the profound influence of Ayn Rand's novels on the literary world and broader society reveals a captivating tapestry of ideas and perspectives that have shaped and challenged traditional norms. Through her compelling storytelling and thought-provoking narratives, Rand's works have left an indelible mark, provoking critical discussions and inspiring individuals across generations.
- Redefining Individualism and Selfishness: Rand's novels champion the importance of individualism and self-interest as catalysts for personal growth and societal progress. Her characters embody the pursuit of rational self-interest, challenging established notions of altruism and emphasizing the value of an individual's aspirations and achievements.
- Proposing a Philosophy of Objectivism: Rand's Objectivist philosophy, intricately embedded within her texts, advocates for reason, egoism, and laissez-faire capitalism. By placing reason at the forefront and championing the pursuit of one's rational self-interest, Rand's works present a unique philosophical framework that critiques collectivism and promotes individual liberty.
- Deconstructing Social Constructs: Rand's novels dissect and challenge prevalent social constructs and ideologies that often stifle individuality and freedom. By delving into themes of government intrusion, societal expectations, and the power dynamics within interpersonal relationships, her works ignite introspection and foster critical thinking about the structures that govern our lives.
- Inspiring Intellectual Dialogue: The enduring impact of Rand's fiction lies in its ability to stimulate intellectual discourse and debate. Her novels have sparked discussions on topics ranging from the nature of morality and the role of government to the importance of personal ambition and the pursuit of happiness. Through these discussions, her ideas continue to shape and influence contemporary philosophical and political discourse.
- Cultivating Empathy and Emotional Resonance: Beyond the philosophical ideas, Rand's novels offer emotionally charged narratives that immerse readers in the lives and struggles of her characters. By weaving intricate storylines and humanizing complex individuals, she enables readers to experience a wide range of emotions, fostering empathy and a deeper understanding of the human condition.
The impact of Ayn Rand's novels on literature and society extends far beyond the realms of fiction. Through her unique perspective, she challenges readers to question prevailing ideologies, and her powerful storytelling leaves an indelible imprint on individuals and society as a whole. The legacy of her work continues to inspire readers to explore their own beliefs, challenge societal norms, and strive for personal growth.
Rand's Revolutionary Concept of Rational Self-Interest

In this section, we delve into the groundbreaking ideas put forth by the enigmatic philosopher and novelist, Ayn Rand, as she unveils her unique perspective on the concept of rational self-interest. Rand's philosophy challenges conventional notions and presents a thought-provoking examination of individualism and its role in society.
Embracing Individualism:
Rand's philosophy celebrates individualism as a fundamental pillar of human nature. She establishes that each person possesses the inherent right to pursue their own self-interest, guided by reason and rationality. Rejecting the notion of selflessness as a virtue, she argues that one's own happiness and well-being should be the central focus.
Rationality as the Guiding Light:
Central to Rand's concept is the importance of rationality in decision-making and the pursuit of self-interest. She emphasizes that only by employing reason and logic can individuals truly understand their own desires and aspirations. Rational self-interest, according to Rand, is a means to achieve personal fulfillment and flourishing, while also benefiting society as a whole.
The Harmony of Interests:
Contrary to popular belief, Rand argues that rational self-interest is not synonymous with greed or exploitation. Instead, she proposes that individuals, pursuing their own self-interest, can create a harmonious society where cooperation and voluntary exchange thrive. Through their self-interested actions, individuals contribute to the overall progress and prosperity of society.
Impact on Political and Economic Thought:
Rand's revolutionary concept of rational self-interest has had a profound influence on political and economic thought. Her advocacy for free-market capitalism and limited government intervention aligns with her belief in the supremacy of individual rights and the pursuit of self-interest. Rand's ideas continue to shape debates and discussions surrounding individual liberty and the role of government in society.
By examining Rand's concept of rational self-interest, we gain valuable insights into the complexities of human nature and the potential for personal and societal growth through individual autonomy and reason.
The Criticisms and Rebuttals of Ayn Rand's Philosophy
In this section, we delve into an examination of the various criticisms that have been raised against the philosophical ideas put forth by the renowned thinker, Ayn Rand. By critically analyzing her ideology, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of the valid concerns and objections that have been voiced by scholars and intellectuals.
| Criticism | Rebuttal |
|---|---|
| 1. Inherent Selfishness: | Contrary to the perception that Ayn Rand advocates for pure selfishness, her philosophy emphasizes rational self-interest as a means of pursuing personal happiness and productivity. It is important to note that she detested the notion of exploiting others or engaging in unethical behavior. |
| 2. Lack of Empathy: | While Ayn Rand prioritized individualism and self-reliance, she did not dismiss the significance of empathy entirely. Her philosophy recognizes empathy as a voluntary choice rather than an obligation, focusing on the affirmation of human flourishing rather than forced altruism. |
| 3. Oversimplification of Human Nature: | Some critics argue that Ayn Rand's philosophy oversimplifies the complex nature of human beings by reducing them to purely rational and self-interested individuals. However, Rand herself acknowledged the presence of emotions and acknowledged the potential conflict between rationality and emotions in human decision-making. |
| 4. Unattainable Ideal: | Detractors claim that Ayn Rand's vision of a society built entirely on the principles of objectivism and rational self-interest is unattainable and unrealistic. However, Rand argued that her philosophy serves as a moral guidepost, encouraging individuals to strive for a higher standard rather than promoting a flawless utopia. |
| 5. Disregard for the Less Fortunate: | Many critics accuse Ayn Rand's philosophy of neglecting those who are less fortunate or marginalized. However, Rand's viewpoint asserts that individual success and achievement can contribute to society as a whole, creating wealth and progress that can be utilized to alleviate poverty and improve the overall standard of living. |
By considering these criticisms and providing counterarguments, we aim to present a well-rounded analysis of Ayn Rand's philosophy and encourage further exploration and debate on the subject.
The Impact of Ayn Rand on Politics and Economics

Exploring the far-reaching influence of a visionary thinker and writer, this section examines the indelible mark left by an extraordinary mind on the realms of politics and economics. Ayn Rand's ideas and philosophies have captivated countless individuals, reshaping their perspectives on governance and economic systems.
- Redefining Capitalism: Ayn Rand's philosophy advocates for a laissez-faire capitalist society, wherein individuals are free to pursue their own self-interest without undue government interference. In adhering to this ideology, Rand challenges the conventional beliefs about the role of the state in regulating economic activities.
- Individualism and Personal Empowerment: Rand's emphasis on individual rights and personal autonomy resonates deeply in the political arena. Her message of self-reliance and the pursuit of rational self-interest has influenced politicians and policymakers, shaping debates on social welfare programs, taxation, and government intervention.
- The Objectivist Movement: Ayn Rand's Objectivist philosophy has gained a fervent following among those seeking to align politics and economics with her principles. This section explores the growth of the Objectivist movement, its impact on political discourse, and its influence on libertarian and conservative ideologies.
- Controversies and Critiques: Just as with any influential figure, Ayn Rand has not been immune to criticism. Addressing the controversies surrounding her ideas and their practical applications, this part delves into the contrasting viewpoints and debates sparked by her political and economic theories.
- A Legacy of Influence: Ayn Rand's influence extends beyond her lifetime, enduring as a source of inspiration for politicians, economists, and activists alike. This section delves into the lasting effects of her ideas on modern-day political and economic thought, examining the ways in which her legacy continues to shape society.
By examining Ayn Rand's impact on politics and economics, we gain a deeper understanding of the lasting effects of her philosophy on the way we perceive and structure our social systems. Her ideas challenge conventional wisdom, sparking debates that continue to shape our political landscape today.
Ayn Rand's Inspiring Female Characters and Feminist Legacy
Exploring the enduring influence of Ayn Rand's works, this section delves into the impact of her captivating female characters and their contribution to feminist ideas. Rand's narratives are populated by strong, determined women who defy societal norms and challenge traditional roles, serving as catalysts for the advancement of women's empowerment.
Within Rand's literary universe, the female characters embody a remarkable range of attributes and beliefs. They exhibit unwavering determination, intellectual prowess, and a deep sense of individualism, showcasing the multidimensional nature of womanhood. Through their actions and convictions, they inspire readers to question societal expectations and pursue their own dreams and aspirations.
Whether it be Dagny Taggart in "Atlas Shrugged," who fearlessly navigates the male-dominated world of railways and demonstrates extraordinary leadership, or Dominique Francon in "The Fountainhead," who resists societal pressures and remains committed to her own principles, Rand's female characters provide a compelling vision of independent women unafraid to challenge established norms.
Furthermore, Rand's portrayal of female characters intersects with feminist ideals by emphasizing the importance of individual liberty and personal fulfillment. These women reject the notion that their worth is solely determined by their relationships with men or their conformity to societal expectations. Instead, they fervently pursue their passions and advocate for their rights as autonomous individuals.
The enduring feminist legacy of Ayn Rand is reflected in the impact her writings have had on subsequent generations. Her fearless exploration of the complexities of womanhood and her rejection of limiting stereotypes have inspired countless women to assert their autonomy, striving for equal opportunities and recognition.
In conclusion, Ayn Rand's engaging female characters and their feminist legacy form an integral part of her enduring literary contributions. By providing readers with powerful and relatable depictions of women who challenge societal expectations, Rand continues to impact generations of readers, encouraging them to strive for personal fulfillment and equal rights.
The Enduring Relevance of Ayn Rand's Ideas in the 21st Century

In today's rapidly changing world, the ideas put forth by Ayn Rand continue to resonate and inspire individuals across the globe. Rand's philosophical principles, centered around rational self-interest and individualism, transcend time and remain relevant even in the technologically advanced and interconnected society of the 21st century.
One of the key tenets of Rand's philosophy is the importance of reason and rationality in guiding human actions and decisions. In an era dominated by information overload and fake news, the need for critical thinking and objective analysis has never been more crucial. Rand's emphasis on the supremacy of reason serves as a beacon of guidance, encouraging individuals to question prevailing narratives and think independently in an era of conformity.
Ayn Rand's celebration of individualism and personal freedom also holds immense relevance in the digital age. With the rise of social media and the constant pressure to conform to societal norms, Rand's ideas remind us of the value of self-determination and the pursuit of one's own happiness. The 21st century presents countless opportunities for individuals to carve their own paths and follow their unique passions, aligning perfectly with Rand's philosophy of rational self-interest.
Furthermore, Rand's belief in the virtues of free-market capitalism continues to be a source of inspiration and debate. As globalization and technological advancements connect the world like never before, the principles of individual freedom, limited government intervention, and voluntary exchange become ever more pertinent. Rand's advocacy for laissez-faire economics offers a powerful counterpoint to the prevailing ideologies, allowing individuals to contemplate the benefits of personal initiative and free markets as catalysts for prosperity.
In conclusion, the ideas of Ayn Rand defy the constraints of time and continue to resonate in the 21st century. Rand's philosophy, encompassing reason, individualism, and free-market capitalism, offers valuable insights and guidance in an era characterized by rapid change and complex challenges. By embracing Rand's principles, individuals can navigate the complexities of the modern world, strive for personal growth, and contribute to a society founded on liberty and individual rights.
Exploring the Limitless Artistry and Innovations of Ayn Rand
Within the realm of creative expression, Ayn Rand emerges as an extraordinary force driven by an inexhaustible wellspring of inspiration. This section delves into the vast artistic works and innovations crafted by this visionary mind, unfolding the depths of her limitless creativity.
FAQ
Who was Ayn Rand?
Ayn Rand, born as Alisa Zinovyevna Rosenbaum, was a Russian-American writer and philosopher. She is best known for her novels "The Fountainhead" and "Atlas Shrugged". Rand's philosophy, known as Objectivism, emphasizes the importance of individualism, reason, and free-market capitalism.
What are some key ideas of Ayn Rand's philosophy?
Ayn Rand's philosophy, Objectivism, promotes rational self-interest, individualism, and the pursuit of personal happiness as the highest moral goals. She believed in the power of reason and free will, and strongly opposed collectivism and altruism. Rand's philosophy also advocates for laissez-faire capitalism and limited government intervention.
How did Ayn Rand's background influence her work?
Ayn Rand's early experiences in Soviet Russia, witnessing the effects of communism and collectivism, greatly shaped her views and writing. She became a fervent advocate for individualism and capitalism as a result of her disillusionment with the oppressive regime. Her personal experiences and observations of the extremes of collectivism influenced the themes and characters in her novels.
What impact did Ayn Rand's novels have on society?
Ayn Rand's novels, particularly "The Fountainhead" and "Atlas Shrugged", have had a significant impact on society and continue to be influential today. Her ideas have attracted a dedicated following and have sparked debates on various topics such as individual rights, capitalism, and the role of government. Rand's novels have also inspired people to question conventional wisdom and to think independently.
How did Ayn Rand's philosophy influence her literary works?
Ayn Rand's philosophy of Objectivism heavily influenced her literary works. Her novels were a medium for presenting and exploring her philosophical ideas. The protagonists in her books often embody the ideals of reason, individualism, and self-interest. Through her characters and their stories, Rand aimed to illustrate the potential of the individual and the importance of rationality and personal freedom.
What were Ayn Rand's major contributions to literature and philosophy?
Ayn Rand made significant contributions to both literature and philosophy. In literature, she wrote influential novels such as "The Fountainhead" and "Atlas Shrugged," which explored themes of individualism, capitalism, and the pursuit of personal happiness. Her philosophy, known as Objectivism, challenged conventional beliefs and promoted rational self-interest, individual rights, and laissez-faire capitalism.
What inspired Ayn Rand to develop her philosophy of Objectivism?
Ayn Rand's philosophy of Objectivism was inspired by her experiences growing up in Russia during the Bolshevik Revolution and witnessing the oppression and collectivism of the Communist regime. Additionally, her admiration for individualism, reason, and capitalism greatly influenced the development of Objectivism, which she saw as an antidote to the oppressive systems she had observed.



